Here is my field!
My research focuses on computerized adaptive testing, insufficient response detection, online calibration, multidimensional item response theory, and cognitive diagnosis models. I am thrilled about the studies advocating equal education. Feel free to contact me, and I cannot wait to share my thoughts with you!
Journal Papers
(* correspondent author, + co-first author)
- Chen, P.*, Dai, Y., Huang, Y. (2023). Test mode effect: Sources, detection, and applications. Advances in Psychological Science, 31(10), 1966–1980. [doi]
- Huang, Y., Ren, H., & Chen, P.* (2023). Item selection methods with exposure and time control for computerized classification test. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, 76, 52-68. [doi]
- Yuan, L., Huang, Y., Li, S., & Chen, P.* (published online). Online calibration in multidimensional computerized adaptive testing with polytomously scored items. Journal of Educational Measurement. [doi]
- Ren, H., Huang, Y., & Chen, P.* (2022). Types, characteristics and application of termination rules in computerized classification testing (in Chinese). Advances in Psychological Science, 30(5), 1168. [doi]
Test mode effect (TME) refers to the difference in test function caused by the administration of the same test in different test modes. The existence of TME will have an impact on test fairness, selection criteria and test equating, so it is of great significance to accurately detect and interpret TME. By systematically sorting out the source, detection (including the experimental design and detection methods) and research results of TME, the methodology of TME research is comprehensively demonstrated. Further interpretation of the TME model, expansion of the test modes in TME research, and application of TME research results to large-scale educational assessment programs in China, are important future development directions in the field of TME.
Computerized classification testing (CCT) commonly chooses items maximizing information at the cut score, which yields the most information for decision-making. However, a corollary problem is that all examinees will be given the same set of items, resulting in high test overlap rate and unbalanced item bank usage, which threatens test security. Moreover, another pivotal issue for CCT is time control. Since both the extremely long response time (RT) and large RT variability across examinees intensify time-induced anxiety, it is crucial to reduce the number of examinees exceeding the time limitation and the differences between examinees' test-taking times. To satisfy these practical needs, this paper proposes the novel idea of stage adaptiveness to tailor the item selection process to the decision-making requirement in each step and generate fresh insight into the existing response time selection method. Results indicate that a balanced item usage as well as short and stable test times across examinees can be achieved via the new methods.
Online calibration is a key technology for item calibration in computerized adaptive testing (CAT), and has been widely used in various forms of CAT, including unidimensional CAT, multidimensional CAT (MCAT), CAT with polytomously scored items, and cognitive diagnostic CAT. However, as multidimensional and polytomous assessment data become more common, only a few published reports focus on online calibration in MCAT with polytomously scored items (P-MCAT). Therefore, standing on the shoulders of the existing online calibration methods/designs, this study proposes four new P-MCAT online calibration methods and two new P-MCAT online calibration designs, and conducts two simulation studies to evaluate their performance under varying conditions (i.e., different calibration sample sizes and correlations between dimensions). Results show that all of the newly proposed methods can accurately recover item parameters, and the adaptive designs outperform the random design in most cases.
Computerized classification testing (CCT) has been widely used in eligibility testing and clinical psychology for its efficiency in classifying participants. As an essential part of CCT, the termination rule determines when the test is to be stopped and what category the participants are ultimately classified into, directly affecting the test efficiency and classification accuracy. According to the theoretical basis of the termination rules, existing rules can be roughly divided into the likelihood ratio, Bayesian decision theory, and confidence interval rules. And their core ideas are constructing hypothesis tests, designing loss functions, and comparing the relative positions of confidence intervals, respectively. Based on these ideas, in different test situations, CCT termination rules have various specific forms. Future research can further extend Bayesian rules, construct rules for multidimensional and multicategory CCT, integrate process data into termination rules, and build rules under the framework of machine learning. In addition, from the perspective of practical requirement, all three types of rules have the potential to be applied in eligibility tests, while the Bayesian rules are optimal to clinical questionnaires.
- Lu, A.+*, Deng, R.+, Huang, Y.+, Song, T., Shen, Y., Fan, Z., & Zhang, J. (2022). The roles of mobile app perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use in app-based Chinese and English learning flow and satisfaction. Education and Information Technologies, 1-22. [doi]
- Huang, Y.+, Deng, R.+, Lu, A.+*, Li, Y., & He, J. (under review). How user perception affects app-based second language learning flow and satisfaction: a mediated moderating model and network analysis.
With the popularity of mobile devices, people are increasingly trying to learn a second language (L2) using mobile applications (apps). The current study examined language learners' perceptions of the usefulness and ease of use of mobile learning apps in relation to language learning flow and satisfaction. University students who were learning Chinese as second language (CSL; n = 183) or learning English as second language (ESL; n = 481) completed scales assessing their perceptions of the apps' usefulness (PU) and ease of use (PEOU), L2 learning flow, and L2 learning satisfaction. Latent profile analysis was used to identify latent groups within CSL learners and within ESL learners, according to their mobile apps perceived usefulness, and perceived ease of use scores. The results showed that: (1) a 3-class solution consisting of a low (least positive) perception group, a medium perception group, and a high perception group was supported in both samples of language learners; (2) in the ESL sample, positive perceptions appeared to have a linear relationship with learning flow and satisfaction; in the CSL sample, this linear relationship was seen for satisfaction but not learning flow. The results of regression analysis validated the moderating role type of language learning plays in the link between PU/PEOU and learning flow and satisfaction with stronger links in ESL learners as compared to CSL learners.
- Ni, Y., Tein, J. Y., Zhang, M.*, Zhen, F., Huang, F., Huang, Y., Yao, Y., & Mei, J. (2020). The need to belong: A parallel process latent growth curve model of late life negative affect and cognitive function. Archives of gerontology and geriatrics, 89, 104049. [doi]
Late life negative affect (NA) often co-occurs with poor cognitive function (CF); however, very little is known about the mechanism of the relationship between them. We examined the longitudinal relationship between NA and CF over a 12-year period and the effects of several related risk factors in a general sample. Five waves of data on Chinese Longitudinal Healthy Longevity Survey (CLHLS) were collected from a total of 1,314 elderly Chinese, aged 60 and over. A parallel process latent growth curve model with two time-invariant covariates and seven time-varying covariates was used to demonstrate the joint trajectories of NA and CF to assess their related factors in the elderly during a 12-year period. Results demonstrated that the late life negative affect co-occurs with cognitive decline and negative affect might be a mutative mental reaction to cognitive dysfunction. Gender difference, exercise benefit, and the “need to belong” effect were observed over time, highlighting the importance of exercise and socialization for older females.
Conference Papers
- Huang, Y., Wang, S., Pan, Y., Lu, X., & Chen, P. (2024, April). A motivation-based cognitive diagnostic model for insufficient responses detection. Talk presented at the Annual Meeting of the National Council on Measurement in Education, Philadelphia, PA. [full paper][slides]
- Yuan, L., Huang, Y., & Chen, P. (2023, July). Online calibration for P-MCAT: A neural network based approach. Talk presented at the International Meeting of the Psychometric Society, College Park, Maryland. [abstract]
- Huang, Y., Zhang, T., & Chen, P. (2022, July). Exploring the Structure of Speed in Cognitive Diagnostic Models. Poster presented at the International Meeting of the Psychometric Society, Bologna, Italy. [abstract]
- Zhang, T., Huang, Y., & Xin, T. (2022, July). An analysis of adaptive learning recommendation based on reinforcement learning. Poster presented at the International Meeting of the Psychometric Society, Bologna, Italy. [abstract]
- Huang, Y., Ren, H., & Chen, P. (2022, April). New Item Selection Designs for Computerized Classification Test. Flash Talk presented at the Annual Meeting of the National Council on Measurement in Education, San Diego, CA, Virtual Meeting. [abstract] [slides]
- Huang, Y., Ren, H., & Chen, P. (2021, October). Stage Adaptive and Timed Item Selection Methods for Computerized Classification Test. Talk presented at the 23rd National Academic Conference of Psychology, Inner Mongolia. [abstract] [slides]
- Ren, H., Huang, Y., & Chen, P. (2021, October). Who Has the Final Say in Computerized Classification Test: Three Types of Termination Rules. Talk presented at the 23rd National Academic Conference of Psychology, Inner Mongolia. [abstract]
- Huang, Y., Chen, P., & Zhang, M. (2021, July). Classification Accuracy and Consistency under Different Maximum Information Locations. Talk presented at the 6th Annual Meeting of National Assessment for Basic Education Quality and Evaluation, Xian. [abstract] [slides]
- Ni, Y., Huang, Y., & Zhang, M. (2018, November). Subtypes of longitudinal association between late life cognitive function and negative affect: a parallel progress growth mixture model. Talk presented at the 21st National Academic Conference of Psychology, Beijing. [abstract]
Projects
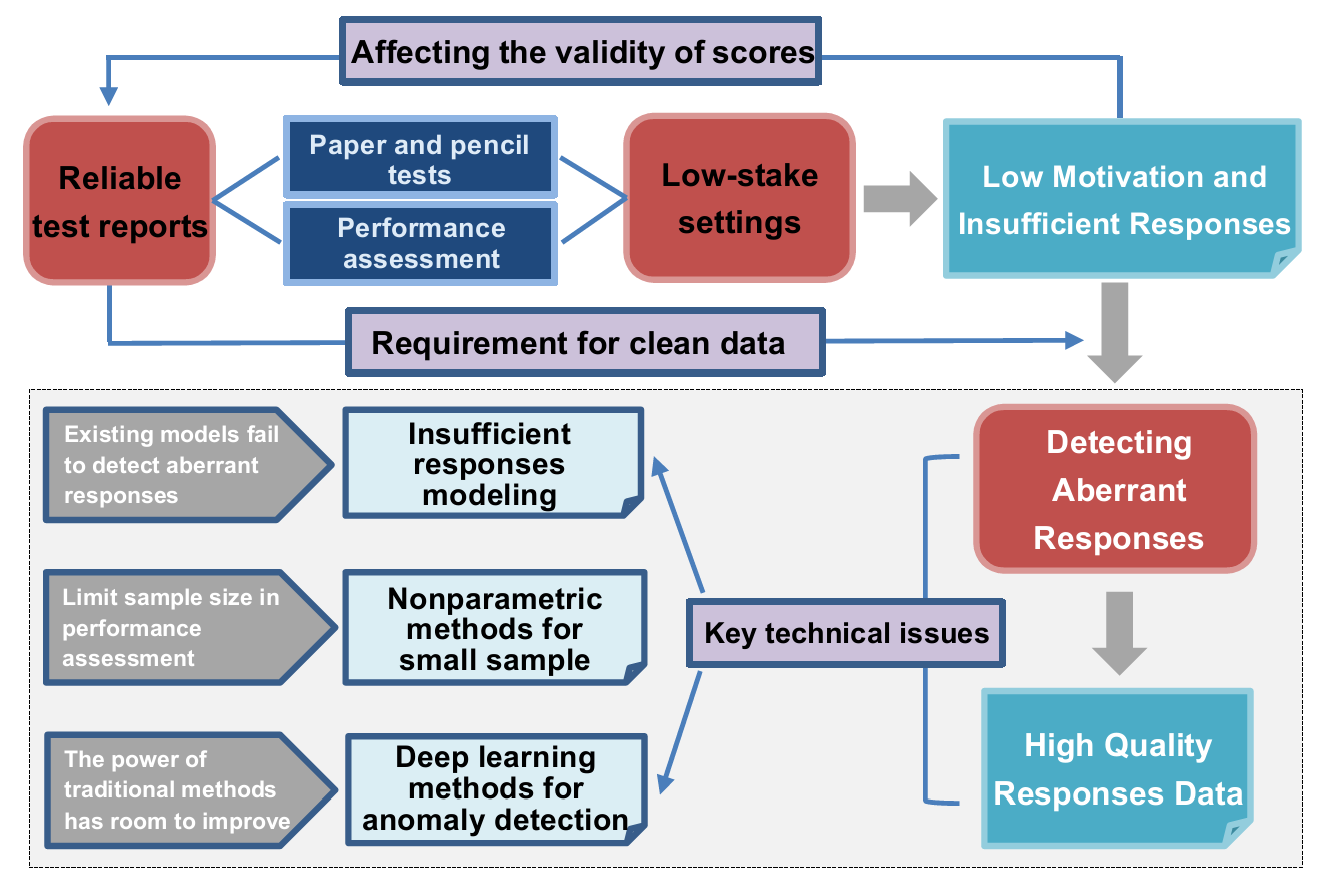
This research project concentrates on detecting aberrant responses in the National Assessment, putting forward
a modeling framework and advanced algorithms to discern insufficient responses in cognitive diagnosis testing,
to improve estimations of parameters with limited sample size, and to apply machine learning to the field of educational assessment.
In this project, I am responsible for the development of a novel cognitive diagnosis model (CDM) detecting insufficient and low-motivated responses.
The new motivated CDM considers both omission and rapid guessing as indicators of examinees' engagement, establishing a connection between examinees' attribute patterns and test-taking motivation.
Principal Investigator: Dr. Ping Chen, Associate Professor, Beijing Normal University
Participants: Lu Yuan (Phd.), Longfei Zhang (Phd.), Jia Li (Phd.), Yingshi Huang, Shuhang Li, Yanfang Pan, Xiangyu Lu, and Xiao Li.
(Grant No. 2022-01-082-BZK01)
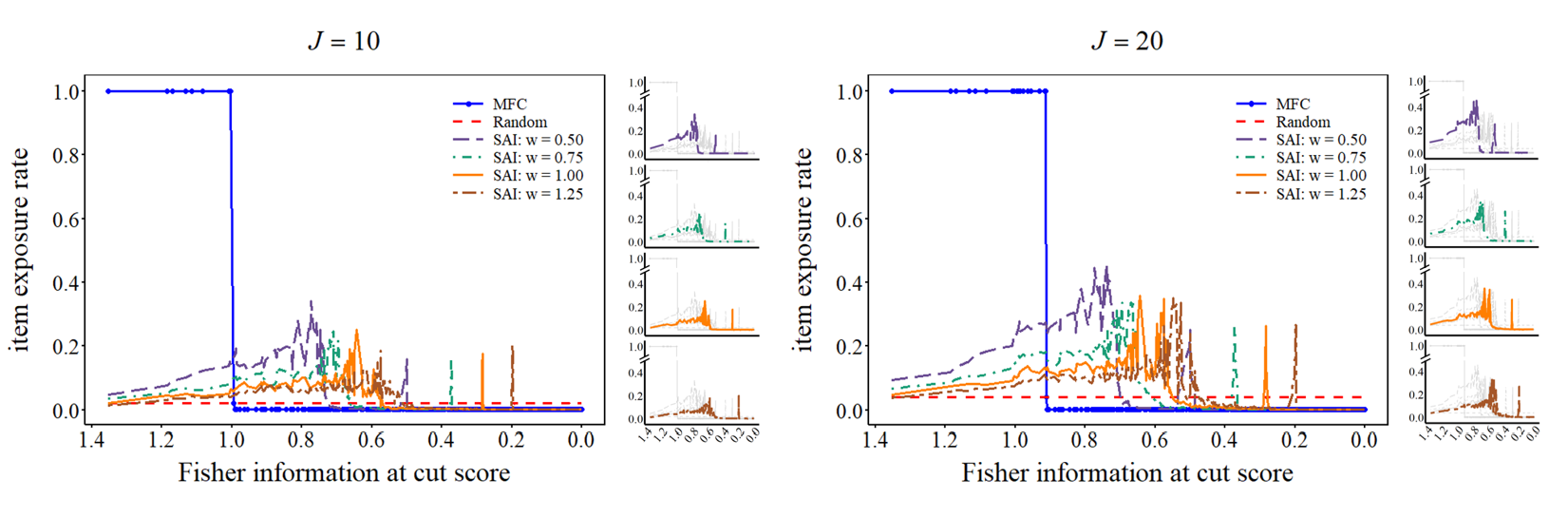
The purpose of this grant is to propose a novel idea of “stage adaptive” to tailor the item selection process with the decision-making requirement in each step and generated fresh insight into the existing response time selection method. Simulations were performed to investigate the item exposure rates, test-taking time, and classification accuracy of new item selection methods under unidimensional and multidimensional scenarios.
Principal Investigator: Yingshi Huang
Participants: He Ren, Mingfeng Xue, Lu Yuan (Phd.), and Jingxi Zhu.
Adivisor: Dr. Ping Chen, Associate Professor, Beijing Normal University
(Grant No. BJZK-2020A2-20011)
Item replenishment plays a pivotal role throughout the construction and maintenance of the item bank, especially for computerized adaptive testing (CAT)
which relies heavily on the high quality of the item bank to secure its function. The primary aim of this project is to develop new online calibration methods
being further effective for complex and realistic scenarios from the perspective of educational measurement models and artificial intelligence. Additionally,
a CAT system will be built to support the implementation and validation of the newly proposed algorithms.
I assisted in programming for Monte Carlo simulations and composed a research paper with Dr. Lu Yuan to introduce new online calibration methods for multidimensional CAT with polytomously scored items.
In addition, I was in charge of updating financial documents and budgets for a year.
Principal Investigator: Dr. Ping Chen, Associate Professor, Beijing Normal University
Participants: Lu Yuan (Phd.), Mingfeng Xue, He Ren, Yingshi Huang, Shuhang Li, and Xiao Li.
(Grant No. 32071092)
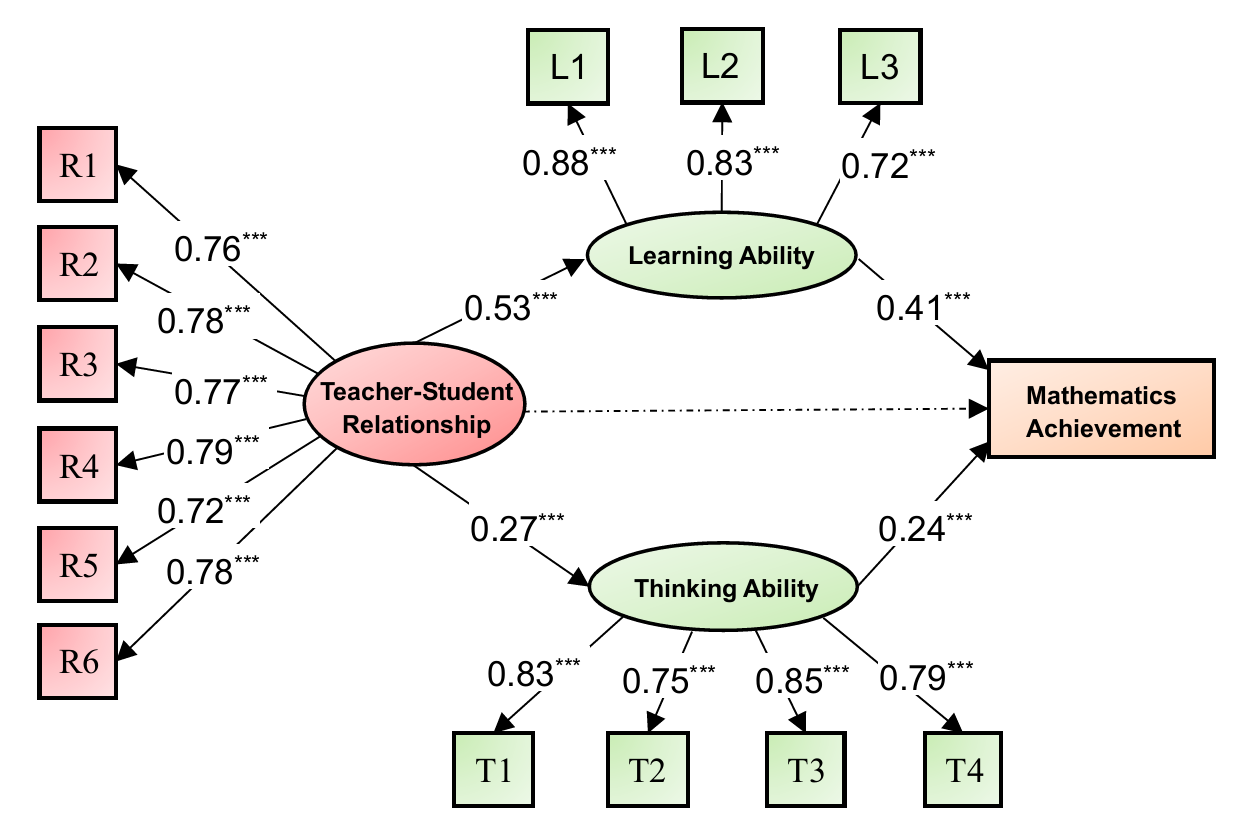
The goal of this project is to ascertain the effect of TSRs on students' mathematics achievement. We collected 3,997 middle school students' responses on the mathematics test and questionnaire batteries. Results revealed that learning ability and thinking ability mediated the relation between the TSRs and the mathematics achievement of middle school students. Interestingly, when we refined students' math achievement into its sub-dimensions (e.g., Algebra ability) and run the model on each dimension, the model fit of several sub-dimensions was suffering, indicating that there may be distinct structures for the relationship between TSRs and different dimensions of mathematics achievement.
Principal Investigator: Yingshi Huang
Participants: Yuhan Ni (Phd.), Fengquan Zhen, and Yiming Yao.
Adivisor: Dr. Minqiang Zhang, Professor, South China Normal University
(Grant No. 19XLGA01)
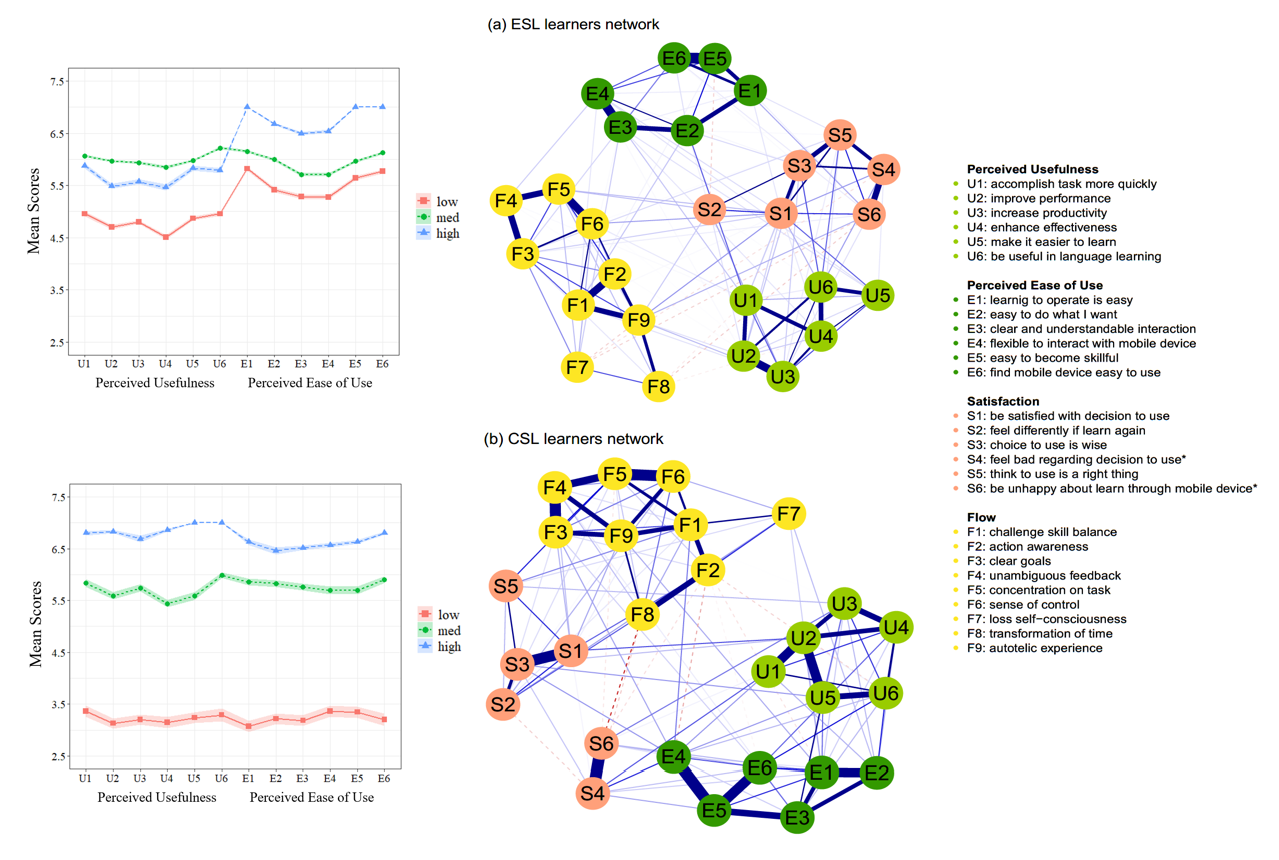
Application (app) -based learning of Chinese and English as a second language (L2) has improved the efficiency of Chinese and English learning and thus becomes popular. The primary goal of this research project is to eyeball the relationship among Chinese and English L2 learners' user perception (i.e., perceived usefulness and ease of use) and learning experience (i.e., learning flow and satisfaction). We collected 786 questionnaires from Chinese learners and English learners and systematically analyzed the data to capture the functioning path from user perception to learning satisfaction and gain a deep understanding of how items or dimensions interact with each other. This project catalyzes our understanding of L2 learning process.
Principal Investigator: Ruchen Deng, Yingshi Huang
Participants: Jingyi He, Ying Huang, Zhiling Fan, Yina Li, Yunhong Shen, and Yingchao Zhang.
Adivisor: Dr. Aitao Lu, Professor, South China Normal University
(Grant No. 18XLGA07)
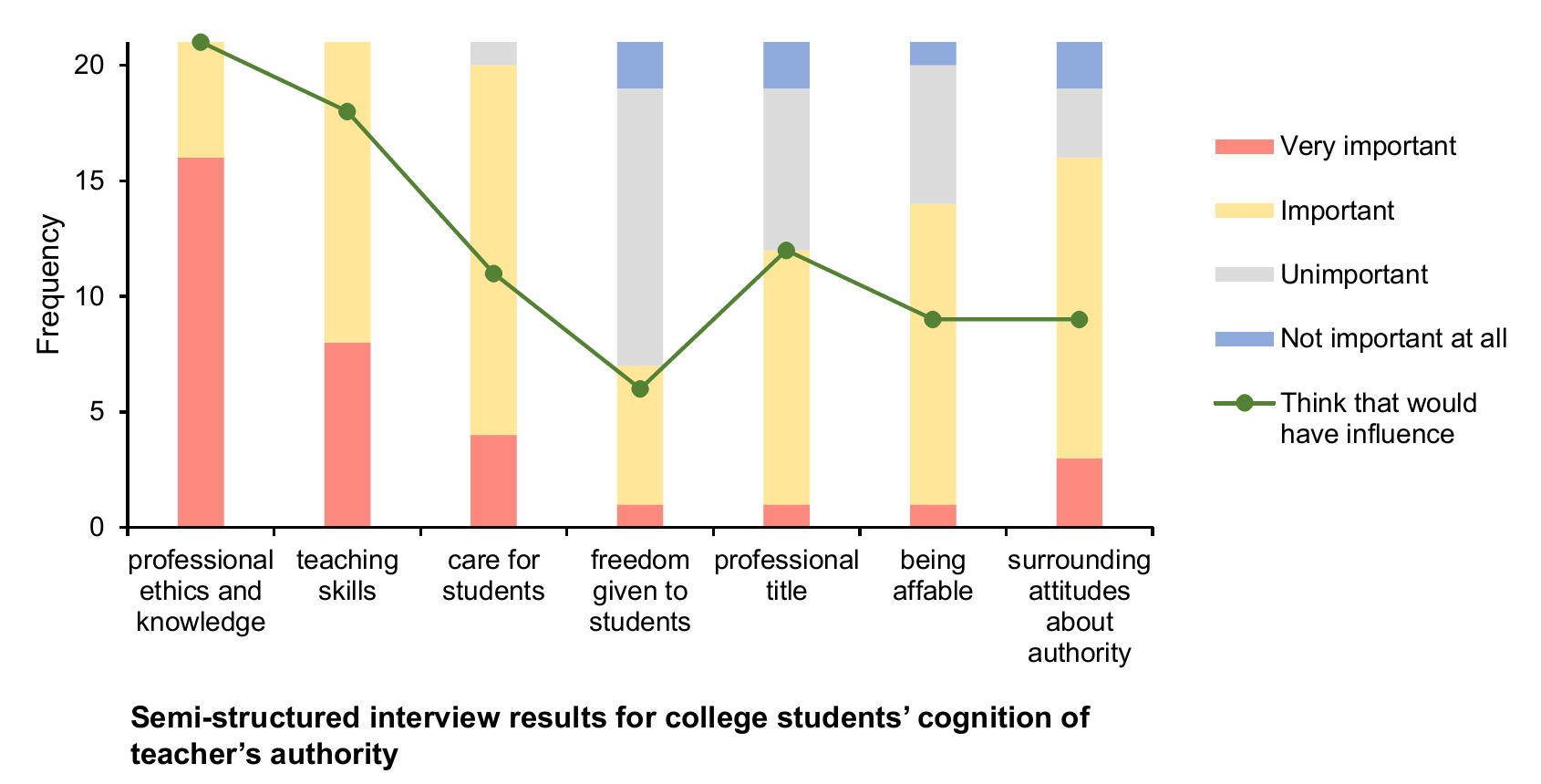
Compared to traditional teaching modes, teachers are not the only source of knowledge nowadays as students have access to a broad range of online search engines. Students' cognition of teacher authority (CTA), especially college students who are given the power to explore their interests, has undergone dramatic changes. In this study, we collected 508 college students to evaluate the reliability and validity of the newly compilated questionnaire. After the revision, we surveyed 245 college students and analyzed the characteristics of their perception of teacher authority. Results showed that college students under different social economic statuses displayed distinct patterns toward the perception of teachers' professional ethics and knowledge. In addition, a three-class solution for CTA was found: highly dependent group, neutral group, and independent group.
Principal Investigator: Yingshi Huang, Zhiling Fan
Participants: Yuxi Fu, Luqi Li, and Yiming Yao.
Adivisor: Dr. Minqiang Zhang, Professor, South China Normal University
(Grant No. XY201812009)
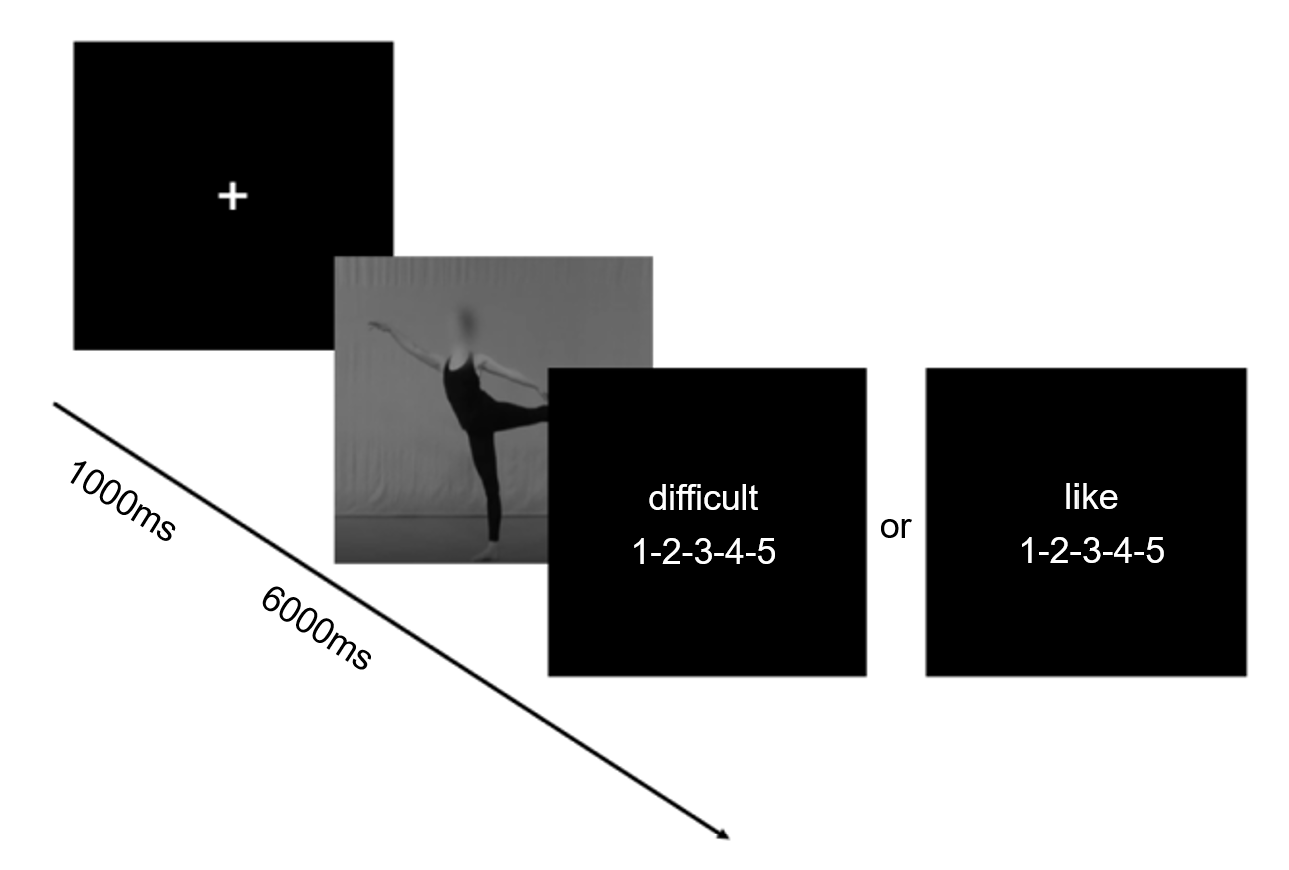
Oxytocin is known to play an important role in a variety of complex social cognitive and emotional functions by promoting prosocial attitudes. In this project, we addressed whether oxytocin could influence dance perception, and observed the activity of individual mirror neurons. To do so, thirty-six participants were administered 24 IU of oxytocin or placebo intranasally in a random, double-blind mixed design. We used EEG MU rhythms as an indicator to observe mirror neuron activity in the aesthetic activities of ballet dance. Three frequency bands of MU were analyzed: 8~10 Hz, the low Alpha band; 10~12 Hz, the high Alpha band; 15~25 Hz, the Beta band. Our findings showed that oxytocin could increase the liking of dance by promoting an individual's positive attention to dance expressiveness and regulating the activity of mirror neurons when perceiving different expressive levels of dance.
Principal Investigator: Ying Huang, Yingshi Huang
Participants: Ruojin Zeng, Zhuangyang Li, and Shihui Jian.
Adivisor: Dr. Xianyou He, Professor, South China Normal University
(Grant No. XY201812001)
